
| COVER STORY | Senior Living is the Way Forward
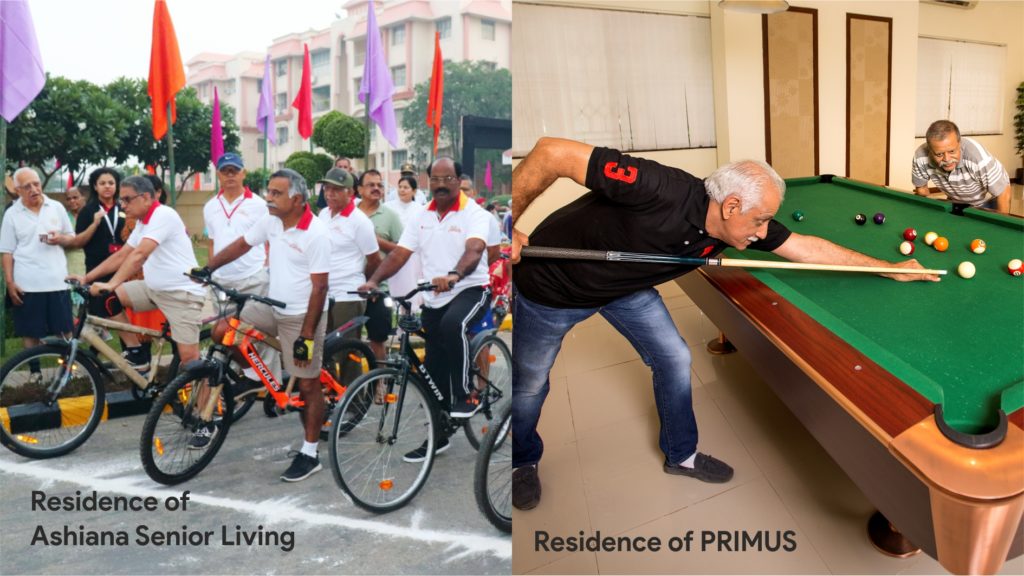

Retirement homes or senior living facilities are safe, secure and fun places to be. A few residents tell us why they opted for it….read more →
| TAKE FIVE | An Eco-Warrior who Inspires One and All
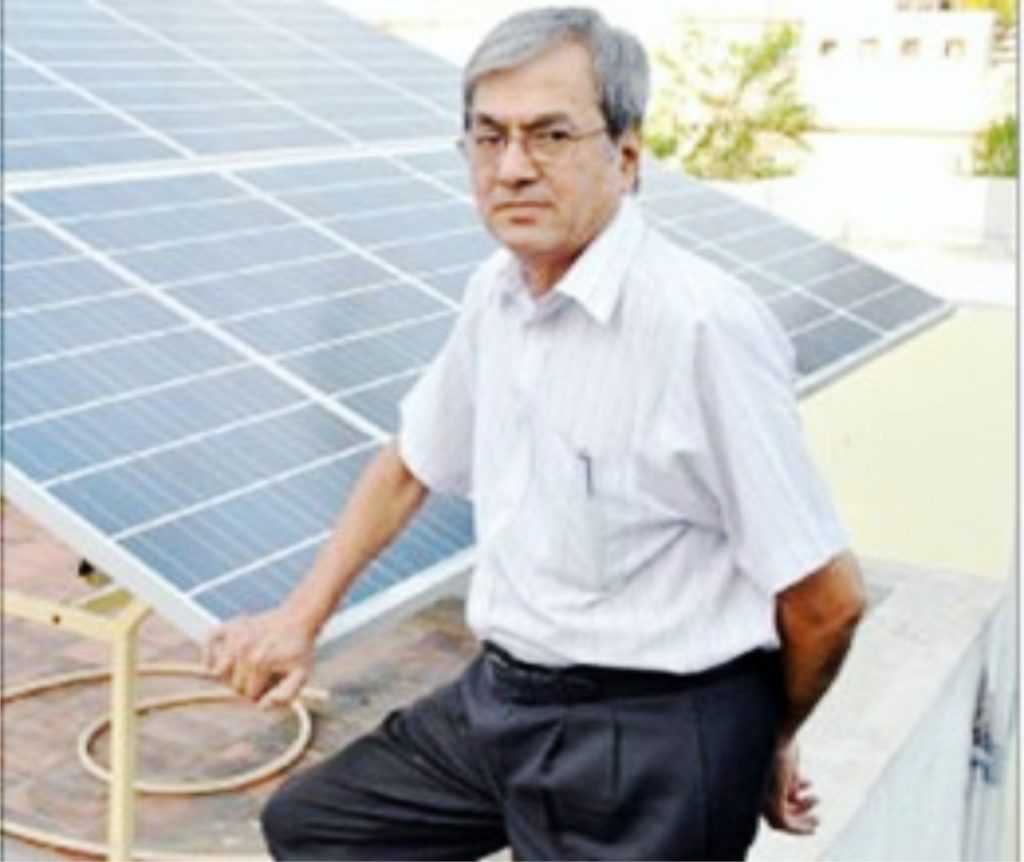

Our senior inspirer, popularly known as ‘Solar Suresh’, wants to leave the planet a beautiful place for future generations…read more →
| UNMUKT RECOMMENDS |
Five Best Books by Indian Writers in 2020

Wrap up the year or start the next year with some of the best in Indian writing of 2020…read more →
The True Worth of Companionship

The ever-popular NYT podcast ‘Modern Love’ is out in a new avatar and it’s a must listen for all reasons and seasons…read more →
| NEWSBRIEFS |
Depression linked to increased risk of Heart Disease and Stroke
People who experience symptoms of depression are more likely to go on to develop heart disease or suffer a stroke, as compared to those who report good mental health, according to a research published recently in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge analysed the health records of over half a million people, with no prior history of heart and circulatory disease, who were enrolled to two different studies: UK Biobank (2006-2010) and the Emerging Risk Factor Collaboration (ERFC; 1960-2008). Upon joining the studies, participants were given a score based on questionnaires assessing their mood and any symptoms of depression that they had experienced over the previous one to two weeks. These scores were divided into five groups based on increasing severity of symptoms.
Now, over 10 years later, researchers have found that those in the highest scoring group, and with most severe symptoms of depression, were more likely to have developed heart disease or to have had a stroke, compared to people with the lowest scores.
(Source: British Heart Foundation)
Study Reveals How Brain Distinguishes Speech from Noise
Scientists have given physiological evidence that a pervasive neuromodulation system – a group of neurons that regulate the functioning of more specialised neurons – strongly influences sound processing in an important auditory region of the brain. The neuromodulator — acetylcholine — may even help the main auditory brain circuitry distinguish speech from noise.
The study, published in the JNeurosci: The Journal of Neuroscience, will bring new attention in the field, highlighting the way circuits like this, widely considered a ‘simple’ one, are in fact highly complex and subject to modulatory influence, similar to higher regions of the brain.
The team conducted electrophysiological experiments and data analysis to demonstrate that the input of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, a pervasive neuromodulator in the brain, influences the encoding of acoustic information by the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body (MNTB), the most prominent source of inhibition to several key nuclei in the lower auditory system.
( Source: National Herald)
| SOCIAL MEDIA |
BLOGS OF THE MONTH
Five Tech Gifts for X’mas
 Still confused what to gift someone this festive season? We give you the best in tech for gifting…read more →
Still confused what to gift someone this festive season? We give you the best in tech for gifting…read more →
Ear, Hear, Clear
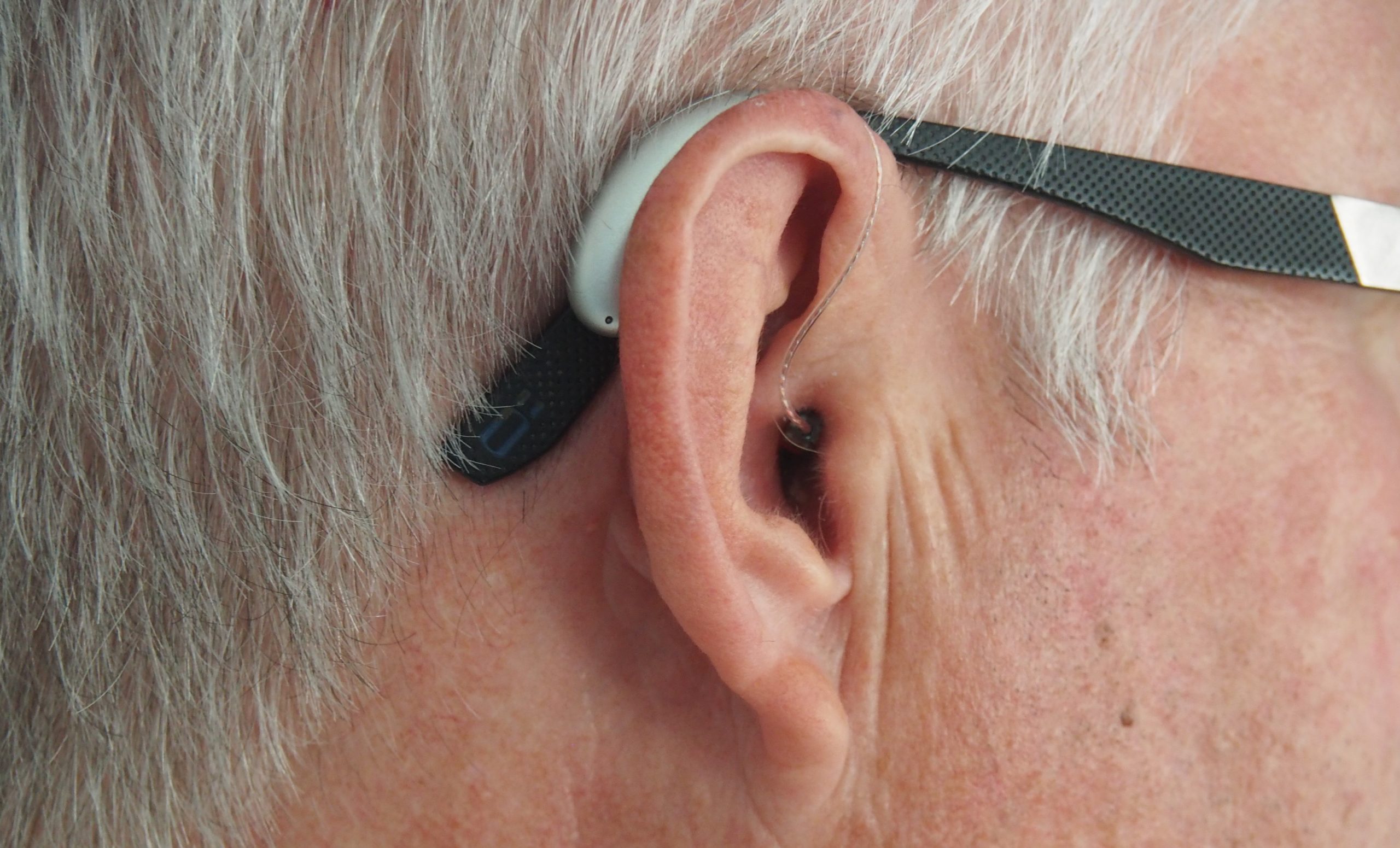 Your hearing health becomes more important as you age. We offer some tips and advice…read more →
Your hearing health becomes more important as you age. We offer some tips and advice…read more →
| UPCOMING EVENTS |

The Seniors Utsav: An online expo by ASLI-Unmukt on 23 & 24 January, 2021 exclusively catering to senior needs.
Become an Unmukt Member, sign up for free


 Learning@Unmukt
Learning@Unmukt